Struggling with emission and tax increase: how the Fiscal Stability Council proposes to rescue the economy
And why Ukraine won’t dispense with international assistance.
On 29 August, the National Bank of Ukraine published its annual report on the activities of the Fiscal Stability Council. This paper covers the period from August 2021 to July 2022. The report’s value is that it shows how main risks and challenges have changed for Ukraine’s economy in general and for its financial sector in particular. Moreover, variants of minimization of these risks and ways of reducing their impact on the economic situation in Ukraine are written there. Mind examined the document and outlined its main accents.
What is the main objective of the Financial Stability Council? This is an interagency body founded by a presidential act as early as in March 2015. Its main objective is to detect potential threats for macrostability and elaborate response measures in case the financial situation of the bank system deteriorates.
Then the National Bank has a right to use the Council’s recommendations for the regulatory purpose, taking measures against banks and other structures that are inferior to the NBU, in particular.
Co-chairmen of the FinStability Council are the Minister of the Finance Sergiy Marchenko and the NBU Head Kyrylo Shevchenko. Members of the Council include representatives of the NBU, the National Securities and Stock Market Commission, Deposit Guarantee Fund and the Office of the President.
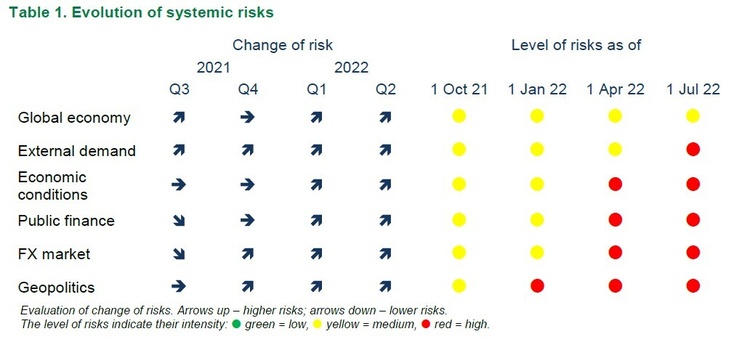
Main risks and their transformation. The NBU notes that the Council estimated systemic risks for the economy and finsector at each meeting (there were four such meetings during the year in total).
And as early as in late 2021, the FinStability Council noticed the aggravation of geopolitical threats related to the eventual military conflict. The Council reviewed the collateral perils immediately after the invasion and concluded, based on the results of the first half of the year, that they are at their highest level.
Source: NBU
The analysis of each mentioned group of risks is mentioned in the report. The long story short, the Council points to this:
- the Ukraine war caused downward revision of the forecast of global economic growth (global GDP, estimated by the International Monetary Fund, will increase by 3.2% thich is almost two times less than in 2021), contraction of world trade, and led to a price hike for food;
- prices for raw materials and energy carriers skyrocketed (natural gas price in Europe has been still near $3000 for 1000 cubic metres). The situation worsened due to logistics issues, as a result of which prices for wheat, corn and vegetable oil reached record-breaking levels, there is till real threat of the global food crisis;
- Ukraine’s GDP drop in 2022 will be no less than 30%. Inflationary pressure will remain high due to the temporary occupation of a part of the territory, disabled producing and transportation infrastructure facilities, disrupted supply chains and increasing costs of entreprises;
- the need for the state budget deficit financing, which occurs mainly thanks to the international donors’ aid and the emission, has increased significantly. At the same time, excessive monetisation of the budget threatens with negative consequences to macroeconomic stability;
- to prevent the swift fall of hryvnia exchange rate the National Bank had had to sell large amounts of currency from its reserve since the end of February. But as of early July the volume of the international reserve remained on the acceptable level and was $22.8 billion (gold and exchange reserves reduced to $22.4 billion by August). The NBU’s active presence on the currency market will continue until prerequisites for market exchange rate regime appear;
- russian invasion facilitated consolidation of the European Union and reinforcing co-operation with Ukraine. Ukraine particularly applied for EU membership and received the candidate country status. Elaboration of the recovery plan for the economy of Ukraine is underway backed by international organisations and partner countries.
Ways of reducing risks and threats. The report says that members of the Council conformed key anti-crisis measures for mitigating the impact of the mentioned risks on the Ukraine economy.
One of the main objectives is to narrow the state budget deficit and lowering its monetary financing. To achieve this it is necessary:
- to conduct optimisation of government expenditures, limiting the non-priority and inefficient directions;
- to find additional sources for increasing budget revenues, firstly at the expense of increasing taxes on import (although, the government rejected the idea to introduce 10% import duty in the end – Mind), exercise duties and rent payments. At the same time, the approach to the tax increase should be weighted, fair and differentiated;
- to promote domestic borrowing through debt instruments (this, naturally, means the domestic government bonds) to finance the state budget;
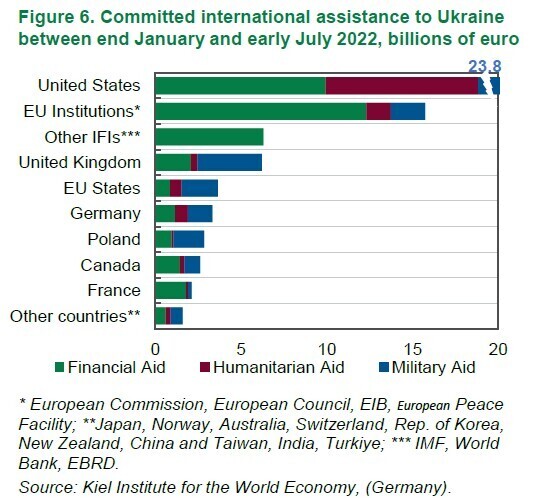
- to instensify efforts for increasing volume of international aid.
Besides, the Council admits, the large support for business for the sake of preserving economic activity in the country is provided by the Affordable Loans 5-7-9% government programme of soft loans. The total amount of loans granted under this programme as of 1 August has reached 133 billion UAH, and 46,000 enterprises and sole proprietors have taken advantage of the loans.
Meanwhile, banks that participate in the 5-7-9 programme admit arrears on compensation of rates of interest. Due to this the Ministry of Finance together with the Foundation for Entrepreneurship Development (FED) intend to do an inspection of preferential programmes for the crediting to occur without failures and indebtedness to banks not to emerge.
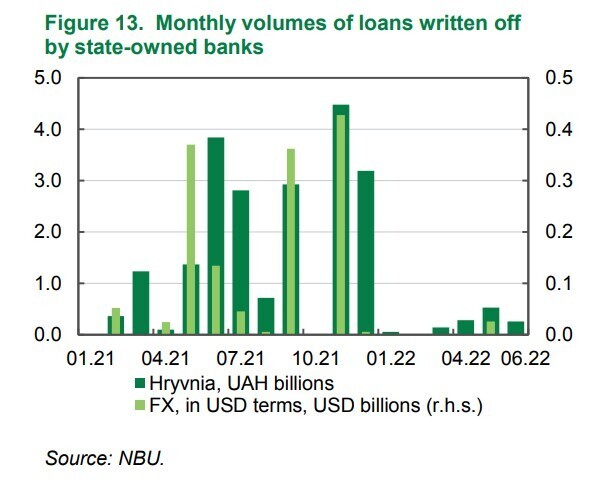
The Council also recommended that government-run banks should more actively clear their credit portfolios from toxic loans (non-performing loans, NPL). Since it is in these fiscal institutions, where the largest number of these NPL is concentrated.
On one hand, state-owned banks did a great work, optimising the problem indebtedness. From the beginning of 2021 to March 2022, 21 billion hryvnia loans and foreign currency loans equivalent to 47.2 billion UAH were written off. Government-owned banks launched over 9 billion UAH loan restructurings for the same period.
Main conclusions. As far as the war became the key challenge for Ukraine, at every its meeting during 2022 the Fiscal Stability Council focused on risks that have been developing amidst the war aggression and concentrated on developing anti-crisis measures.
Given this, the primary goals for the nearest past are: reducing monetary funding of the budget and shortening the state treasury deficit; increasing actual (not only declared) assistance from donors from abroad; business support programmes development; timely fulfilment of its liabilities to banks on the side of the MinFin for them to be interested in taking part in these programmes; constraining problem indebtedness increase (NPL).
